WHY are some people left-handed?
What did some older left-handed people have to do when they were younger?
What does the word right also mean in many languages besides English?
About what fraction of the world’s population is left-handed today?
How far back does archaeological evidence show that people were left-handed?
Can handedness be predicted before birth? If so, what is it based on?
Do identical twins always have the same dominant hand?
If a father is left-handed and a mother is right-handed, what is the chance their child will be left-handed?
What activity shows the clearest benefits of being left-handed?
About what percentage of top hitters in baseball have been left-handed?
Why do left-handed athletes sometimes have an advantage over right-handed athletes?
• Read •
WHY are some people left-handed?
RIGHT = GOOD
If you know an older left-handed person, chances are they had to learn to write or eat with their right hand. And in many parts of the world, it’s still common practice to force children to use their “proper” hand.
Even the word right also means correct or good—not just in English, but in many other languages, too. But if being left-handed is so wrong, then why does it happen in the first place?
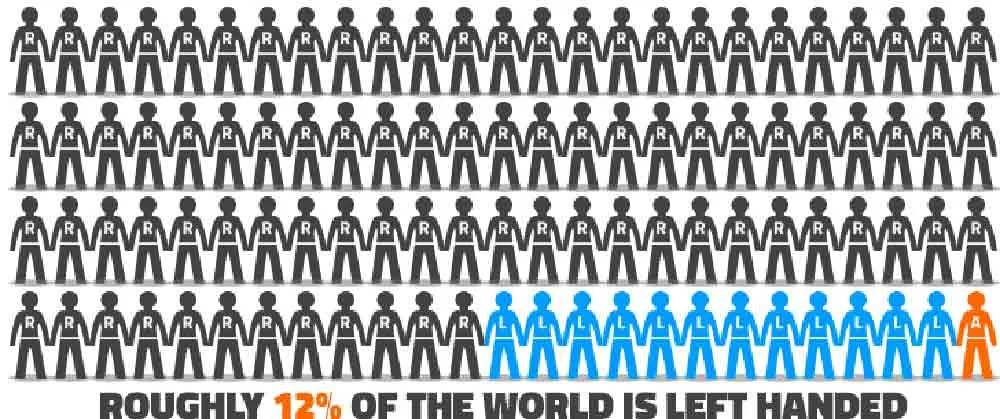
THE 10-12 PER CENT
Today, about one-tenth (10-12%) of the world’s population is left-handed.
Archaeological evidence shows that it has been that way for as long as 500,000 years, with about 10% of human remains showing the associated differences in arm length and bone density, and some ancient tools and artifacts showing evidence of left-hand use.
And despite what many may think, handedness is not a choice. It can be predicted even before birth, based on the fetus’ position in the womb.
GENETIC?
So, if handedness is inborn, does that mean it’s genetic? Well, yes and no.
Identical twins, who have the same genes, can have different dominant hands. In fact, this happens as often as it does with any other sibling pair.
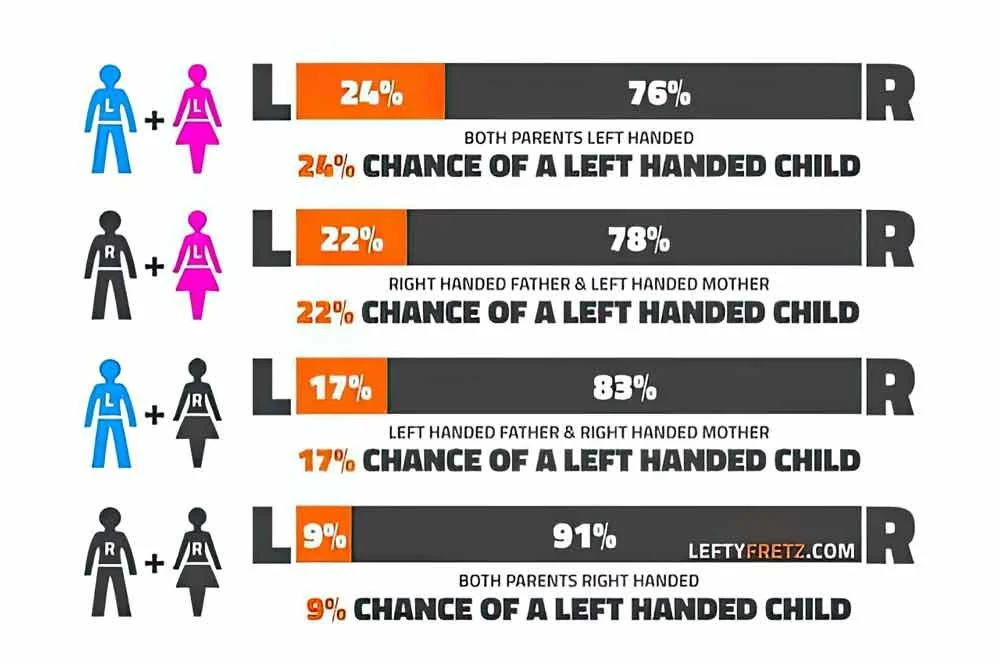
But the chances of being right- or left-handed are determined by the handedness of your parents in surprisingly consistent ratios.
If your father was left-handed but your mother was right-handed, you have a 17% chance of being born left-handed, while two right-handed parents will have a left-handed child only 9-10% of the time.
Handedness seems to be determined by a roll of the dice, but the odds are set by your genes.
BUT WHY?
All of this implies there’s a reason that evolution has produced this small proportion of lefties and maintained it over the course of millennia.
And while there have been several theories attempting to explain why handedness exists in the first place, or why most people are right-handed, a recent mathematical model suggests that the actual ratio reflects a balance between competitive and cooperative pressures on human evolution.
The benefits of being left-handed are clearest in activities involving an opponent, like combat or competitive sports.
For example, about 50% of top hitters in baseball have been left-handed.
This “fighting hypothesis”
Think of it as a surprise advantage.
Because lefties are a minority to begin with, both right-handed and left-handed competitors will spend most of their time encountering and practicing against righties.
So when the two face each other, the left-hander will be better prepared against this right-handed opponent, while the righty will be thrown off.
This “fighting hypothesis,” where an imbalance in the population results in an advantage for left-handed fighters or athletes, is an example of negative frequency-dependent selection. But according to the principles of evolution, groups that have a relative advantage tend to grow until that advantage disappears.
If people were only fighting and competing throughout human evolution, natural selection would lead to more lefties surviving—until there were so many of them that it was no longer a rare asset.
So in a purely competitive world, 50% of the population would be left-handed.
COOPERATION AND COMPETITION
But human evolution has been shaped by cooperation as well as competition. And cooperative pressure pushes handedness distribution in the opposite direction.
In golf, where performance doesn’t depend on the opponent, only 4% of top players are left-handed—an example of the wider phenomenon of tool sharing.
Just as young potential golfers can more easily find a set of right-handed clubs, many of the important instruments that have shaped society were designed for the right-handed majority.
Because lefties are worse at using these tools and suffer from higher accident rates, they would be less successful in a purely cooperative world, eventually disappearing from the population.
EQUILLIBRIUM
So, by correctly predicting the distribution of left-handed people in the general population, as well as matching data from various sports, the model indicates that the persistence of lefties as a small but stable minority reflects an equilibrium that comes from competitive and cooperative effects playing out simultaneously over time.
And the most intriguing thing is what the numbers can tell us about various populations.
From the skewed distribution of pawedness in cooperative animals to the slightly larger percentage of lefties in competitive hunter-gatherer societies, we may even find that the answers to some puzzles of early human evolution are already in our hands.
Accident (n.) something that happens unexpectedly and causes harm or damage.
Advantage (n.) something that helps you do better than others.
Archaeological (adj.) related to the study of old objects, bones, and remains from the past.
Artifact (n.) an object made by humans long ago, often found by archaeologists.
Associated (adj.) connected or linked to something else.
Cooperative (adj.) working together with others toward a common goal.
Distribution (n.) the way something is spread out or shared among a group.
Dominant (adj.) stronger, more powerful, or more in control than others.
Equilibrium (n.) a balance where different forces are equal or steady.
Evolution (n.) the process by which living things slowly change over long periods of time.
Fetus (n.) a baby animal or human before it is born.
Frequency (n.) how often something happens.
Genetic (adj.) related to the parts of our body (genes) that are passed down from parents to children.
Hypothesis (n.) an idea or guess that scientists test to see if it is true.
Majority (n.) the larger part of a group.
Millennia (n.) thousands of years.
Minority (n.) the smaller part of a group.
Predicted (v.) said or guessed that something would happen in the future.
Proportion (n.) the amount of something compared to the whole.
Selection (n.) the process of choosing or being chosen; in science, it means how certain traits survive over time.
► COMPREHENSION QUESTIONS
— please answer with complete sentences
What did some older left-handed people have to do when they were younger?
What does the word right also mean in many languages besides English?
About what fraction of the world’s population is left-handed today?
How far back does archaeological evidence show that people were left-handed?
Can handedness be predicted before birth? If so, what is it based on?
Do identical twins always have the same dominant hand?
If a father is left-handed and a mother is right-handed, what is the chance their child will be left-handed?
What activity shows the clearest benefits of being left-handed?
About what percentage of top hitters in baseball have been left-handed?
Why do left-handed athletes sometimes have an advantage over right-handed athletes?
► From EITHER/OR ► BOTH/AND
► FROM Right/Wrong ► Creative Combination
THESIS — Argue the case that it’s just terrible to be-left-handed in a right-handed world.
ANT-THESIS — Argue the case that it’s great to be left-handed in a right-handed world.
SYN-THESIS — Can both perspectives be true?